One of the mandates of modern central banks is to provide sufficient liquidity to the system as a result of being the lender of last resort. According to central bank law, the underlying objective is to eliminate any problems that may occur in electronic fund transfer system. Since central banks accepted setting short-term nominal interest rate as the appropriate instrument of monetary policy, the simplest system for controlling short-term interest rates is with a symmetric standing facilities corridor around the target rate. Open market operations are monetary policy operations conducted at the initiative of the central bank in order to achieve its operational target of monetary policy. Standing facilities are, in contrast to open market operations, monetary policy operations conducted at the initiative of banks.
Total amount of funding needed in the system is not an easy concept for ordinary economists who are not familiar with treasury operations. Some of them mix central bank funding with central bank reserves which is totally different in nature.
What causes the need for central bank funding ? Basically it is the business model of banking which is illiquid in nature. Banks give loans and collect deposits and try to make profit out of spread between the two. This spread is called net interest margin. Spread is justified with the maturity transformation function of the banks. At this point, central banks is mandated as the lender of last resort to safeguard the financial system’s liquidity.
What determines the amount needed for central bank funding? For most of the central banks, ‘autonomous factors’ explain the amount needed and main items are :
– cash in circulation
– net government balances
– net foreign assets
Under normal conditions, funding need of the system is expected to be equal to reserves of banks with the central bank.
Central Bank Turkey – Net Funding
From now on, we will make some calculations to analyze net funding and how it evolved in 2020. Turkish lira net funding balance (ticker: TP.APIFON3) is available at Data Central. As of October 2020, net funding increased by 216 Billion Turkish Liras.
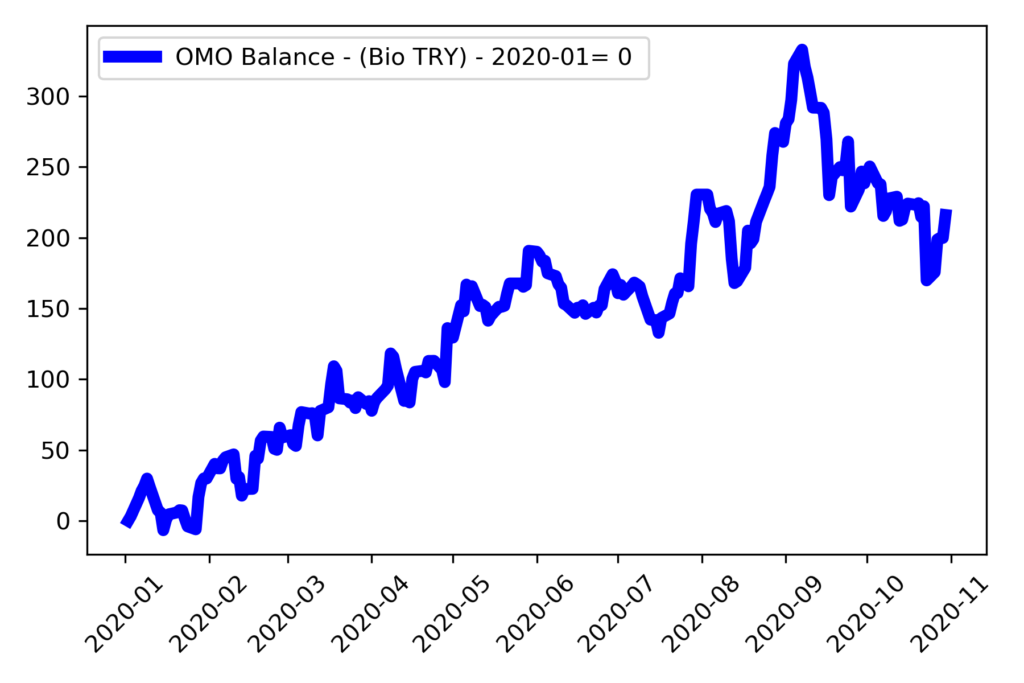
Changes in net funding is related to the transactions that cause banks to lose Turkish Lira liquidity. At first place comes the foreign exchange transactions that cause increase in the need for central bank funding. Increase in derivative transactions of the central bank is also related to it.
FX Swap Liquidity
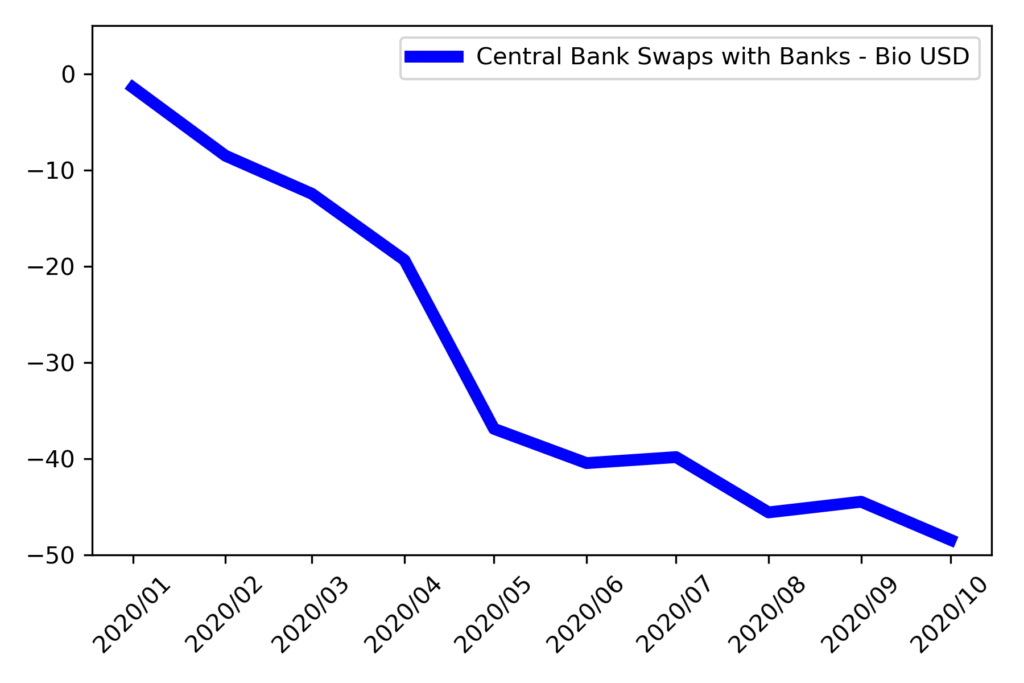
Turkish banks place foreign currency ( ticker: TP.DOVVARNC.K15) and gold (ticker: TP.DOVVARNC.K23) and receive Turkish Lira funding when they enter FX swap transaction with the central bank. Central bank publishes total outstanding fx swap balance at international reserves and foreign currency liquidity table which is prepared within the framework of the Special Data Dissemination Standards – SDDS – set by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). As of October 2020, fx/gold swap outstanding balance increased by 48.4 Billion USD which is equal to 393 Billion Turkish Liras with 8.12 TL per 1 USD.
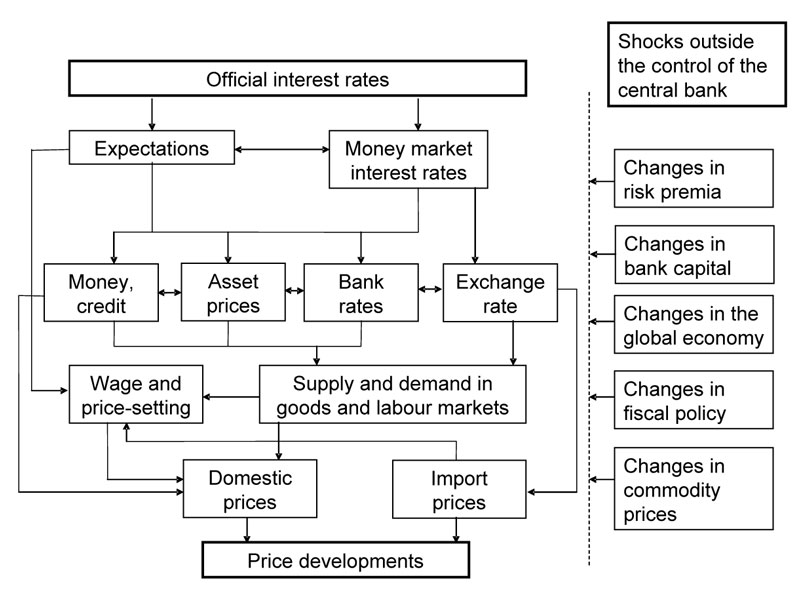
Transmission mechanism on monetary policy is the process through which monetary policy decisions affect the economy in general and the price level in particular. The transmission mechanism is characterised by long, variable and uncertain time lags. Thus it is difficult to predict the precise effect of monetary policy actions on the economy and price level.
Heterogeneity and broken transmission channel
The role of the banking sector in the transmission of monetary policy has been studied in great detail in both the theoretical and empirical literature. If a bank’s characteristics are related to its ability to access non-deposit financing sources, then the existence of a lending channel implies that lending responses to monetary policy are related to bank characteristics.
There are three types of short term non-deposit financing sources reported by Turkish banks.
| Billion TL | Public Banks | Private Banks |
| Payables to Money Market | 143 | 12 |
| Payables to Banks | 70 | 29 |
| Funds From Repo Transactions | 93 | 48 |
| TOTAL | 306 | 89 |
In 2020, public banks increased short term non-deposit financing balance by 276 Billion TL and private banks increased by 23 Billion TL. Although net funding need increased in 2020 causing tight liquidity conditions, public banks increased their lending and enjoyed short term cheap funding.
