Implementing Stability and Growth Strategies under Mehmet Şimşek, Minister of Treasury and Finance
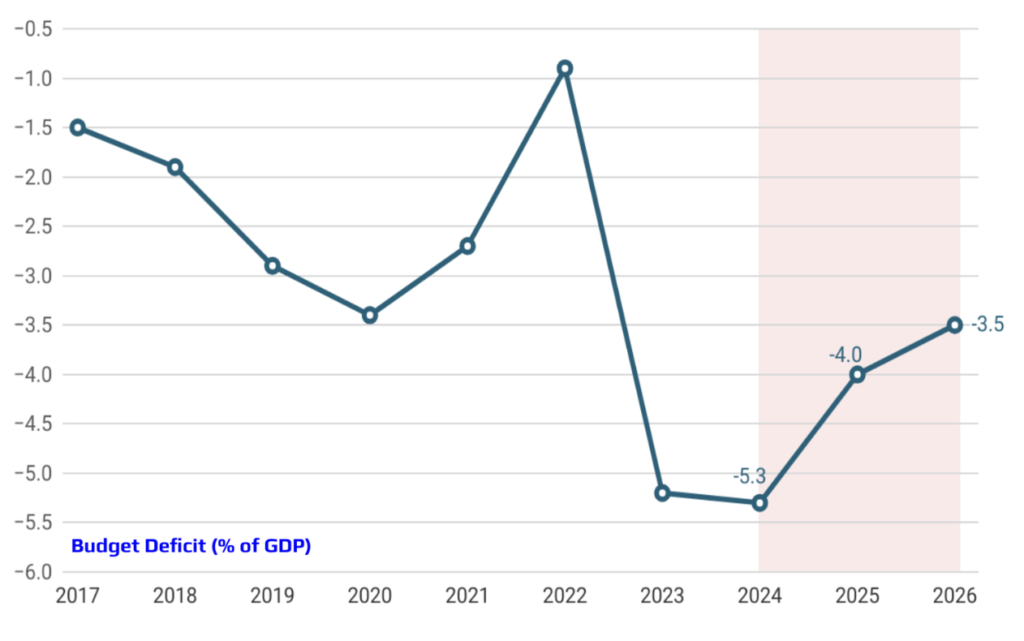
Mehmet Şimşek, as the Minister of Treasury and Finance, leads a team dedicated to implementing a Neo-Keynesian macroeconomic policy framework. This approach prioritizes achieving a delicate balance between price stability and financial stability while anchoring inflation expectations. By maintaining disciplined public finances and promoting an effective financial system, the team aims to ensure sustainable economic growth and stability. As Turkey navigates through complex economic conditions, the emphasis on prudent fiscal management, balanced foreign trade, and a well-functioning financial system will be key. These pillars not only support the domestic economy but also build investor confidence, positioning Turkey as a resilient player on the global stage.

A Roadmap for Price Stability
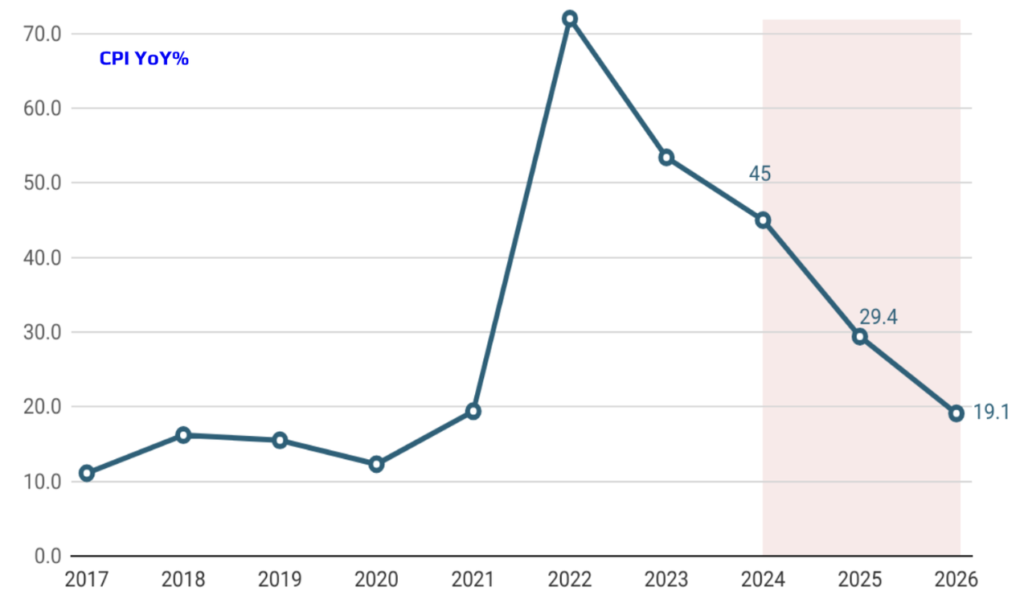
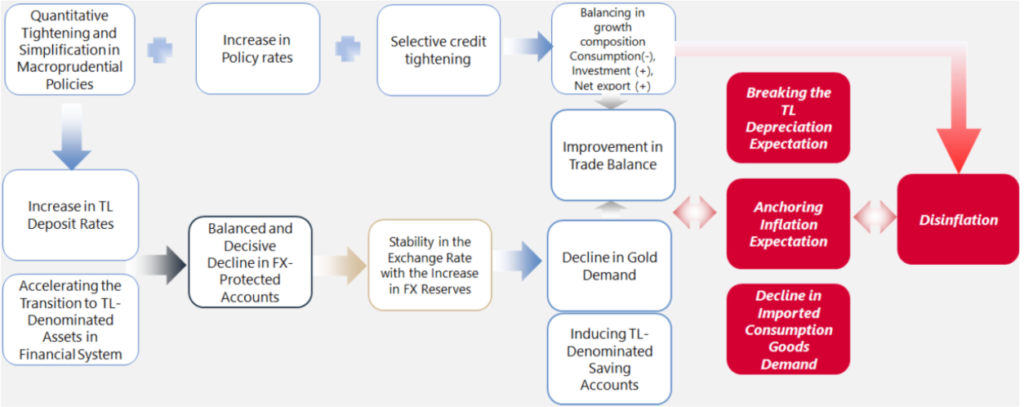
Under the leadership of Central Bank Governor Fatih Karahan, a comprehensive roadmap for price stability has been developed to combat inflation and ensure sustainable economic growth. This strategy focuses on the coordinated implementation of monetary and fiscal policies to achieve macroeconomic stability. Key elements include enhancing the effectiveness of the monetary policy transmission mechanism by using interest rate hikes and tighter financial conditions to reduce inflation expectations. The roadmap also anticipates a gradual increase in credit interest rates and a significant slowdown in selective lending to balance excess demand and alleviate inflationary pressures. Additionally, measures to increase foreign exchange liquidity and promote de-dollarization are being implemented to strengthen confidence in the Turkish Lira by reducing commercial and retail FX deposits. This balanced approach aims to anchor inflation expectations, maintain fiscal discipline, and establish an efficient financial system, paving the way for a more sustainable and predictable economic structure for Turkey.
Effective Monetary Policy Transmission for Economic Stability
The Central Bank’s monetary policy transmission mechanism plays a critical role in shaping economic conditions by influencing short-term interest rates and overall financial stability. By adjusting the policy rate, the Central Bank directly impacts the cost of borrowing and the attractiveness of saving, which in turn affects consumer spending, investment, and ultimately inflation. When the Central Bank raises policy rates, it signals a tighter monetary stance, leading to higher borrowing costs and encouraging savings over spending. This helps to curb excess demand and control inflationary pressures. Conversely, lowering policy rates makes borrowing cheaper and can stimulate economic activity. This mechanism ensures that monetary policy decisions effectively permeate through the economy, influencing a wide range of financial variables and helping to achieve key objectives such as price stability and sustainable growth.
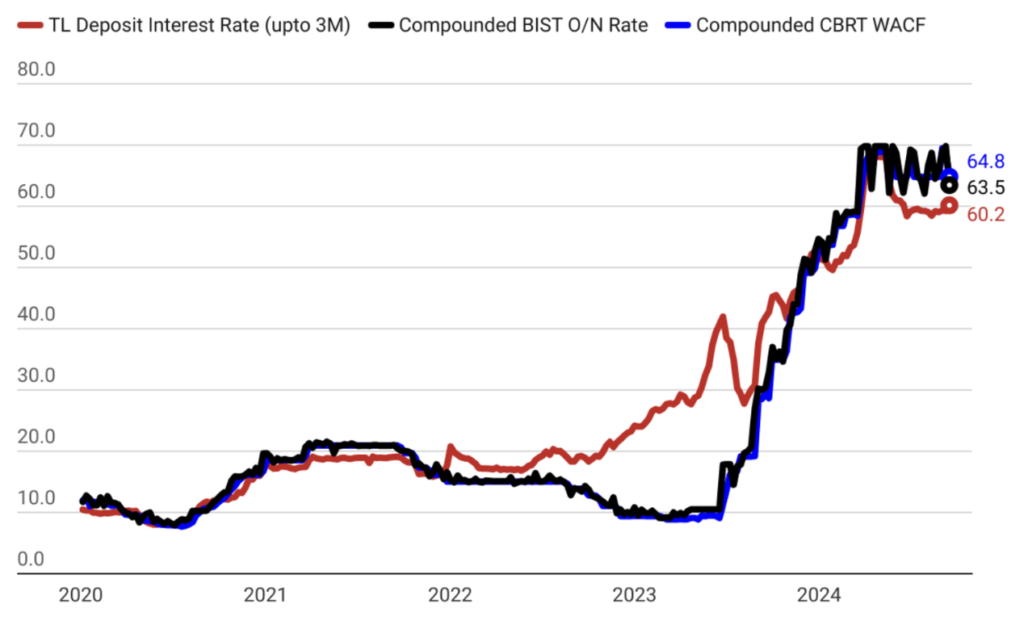
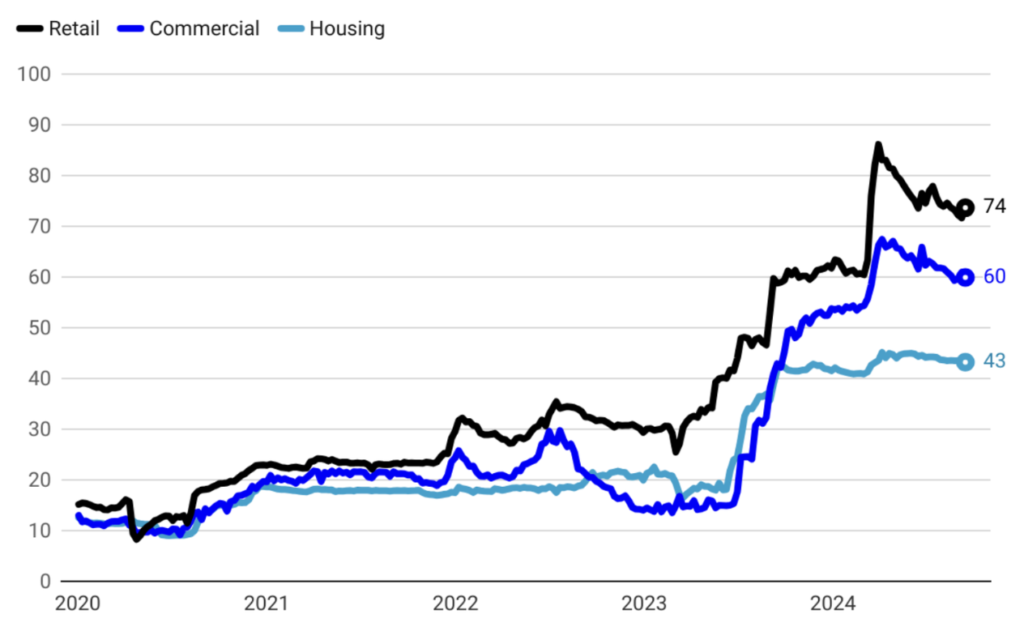
Controlling Credit Growth for Economic Stability
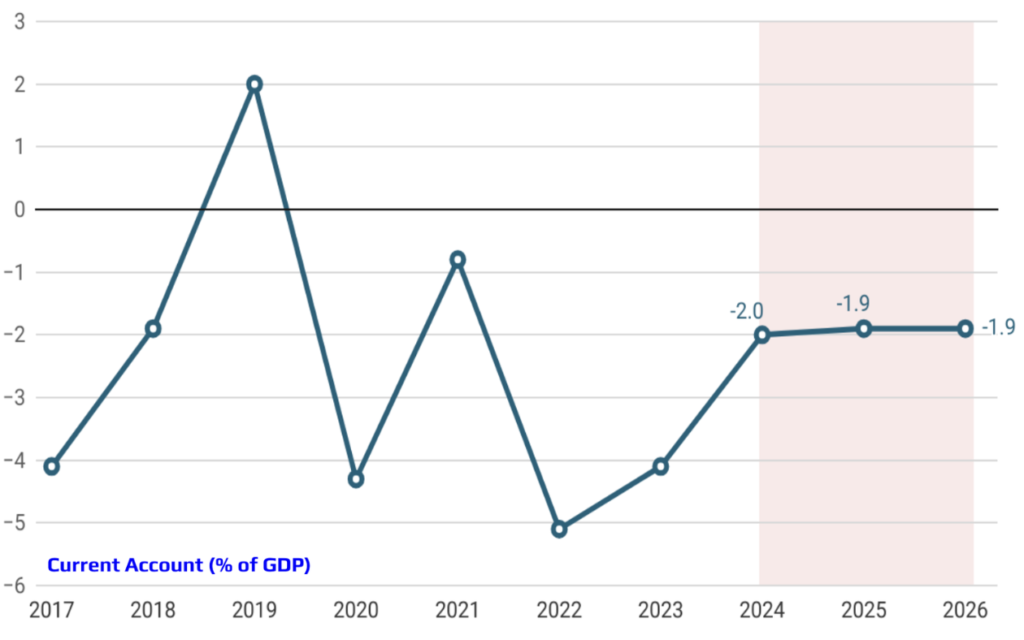
In Turkey, an uncontrolled surge in credit growth can lead to significant challenges, including rising inflation and an expanding trade deficit. Rapid credit expansion often fuels consumer demand and import activity, putting upward pressure on prices and worsening the trade balance. Recognizing these risks, the Central Bank has recently implemented measures to slow down credit growth. Through tighter monetary policies and selective lending restrictions, the Central Bank has successfully curbed the pace of credit expansion, thereby mitigating inflationary pressures and contributing to a more balanced external trade position. These actions are crucial for maintaining economic stability and ensuring sustainable growth in the long term.
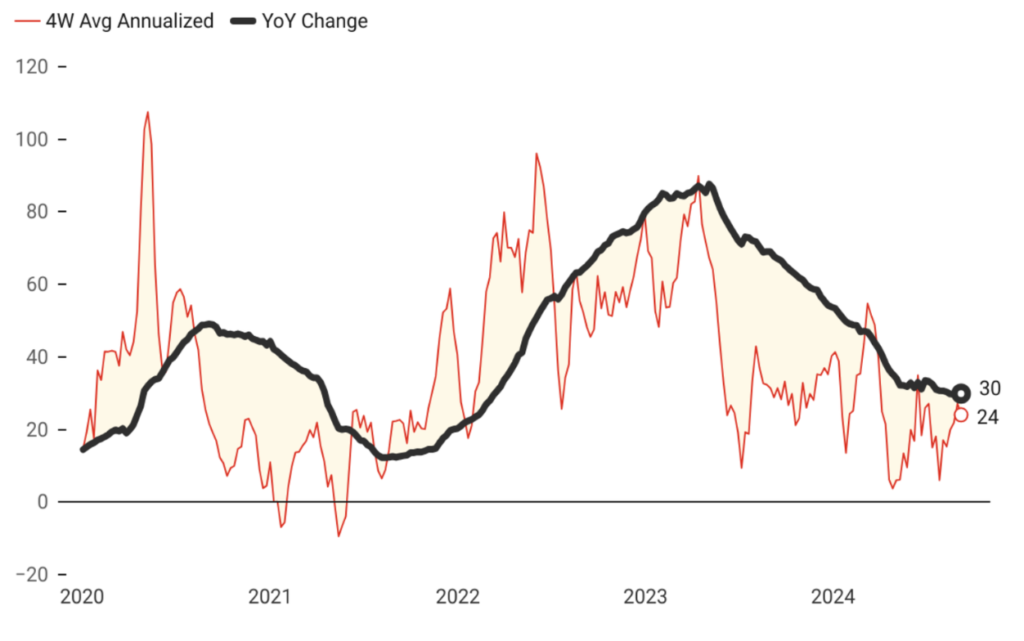
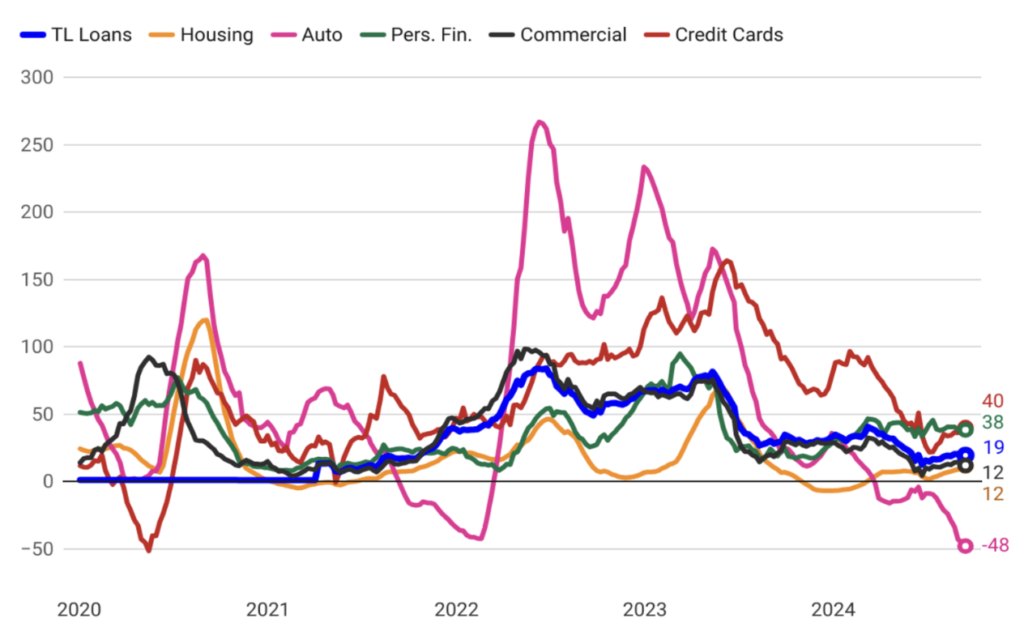
Supporting De-dollarization and Phasing Out FX-Protected Deposits
The implemented policies have played a crucial role in supporting the de-dollarization process and achieving significant progress in phasing out FX-protected deposits. By promoting confidence in the Turkish Lira and tightening monetary conditions, the Central Bank has encouraged both individuals and businesses to shift away from holding foreign currency deposits. This strategic shift not only reduces the economy’s vulnerability to exchange rate fluctuations but also strengthens the domestic financial system. The gradual reduction and eventual elimination of FX-protected deposits mark a critical milestone in this transition, aligning with the broader goal of enhancing monetary stability and reinforcing trust in the local currency.
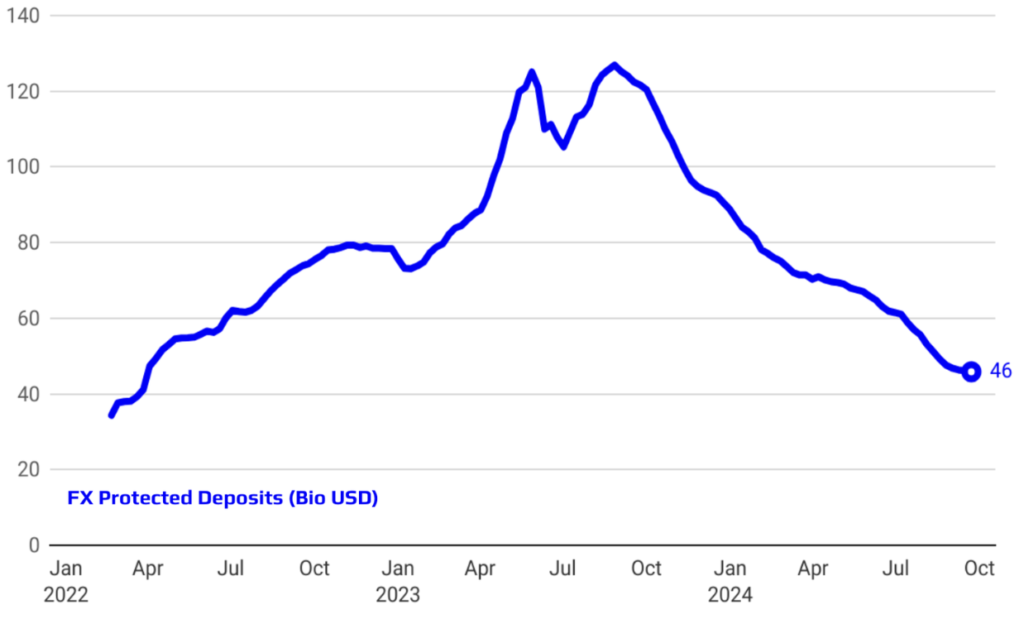
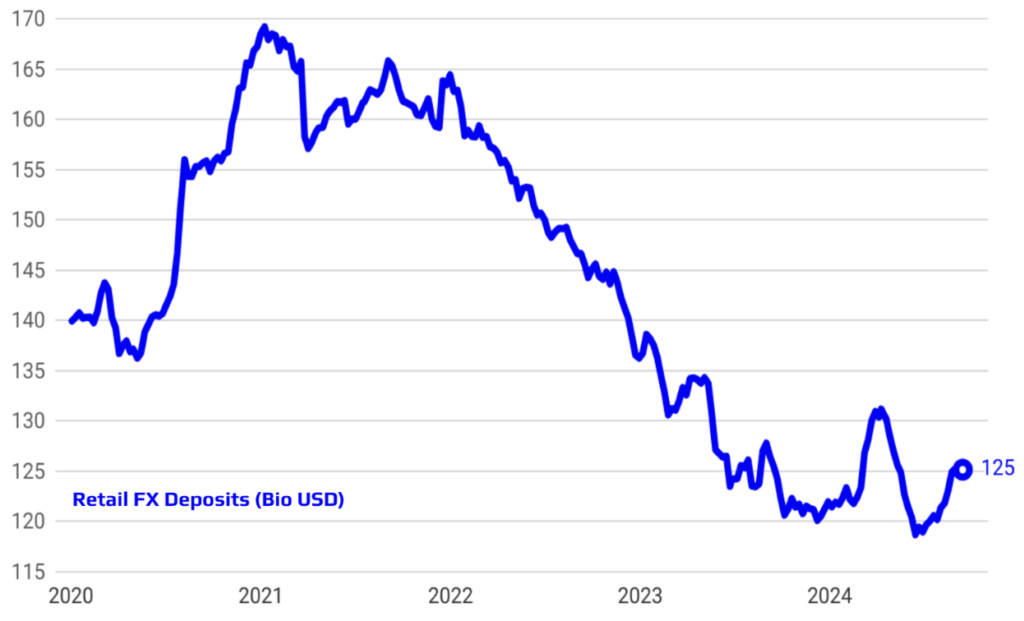
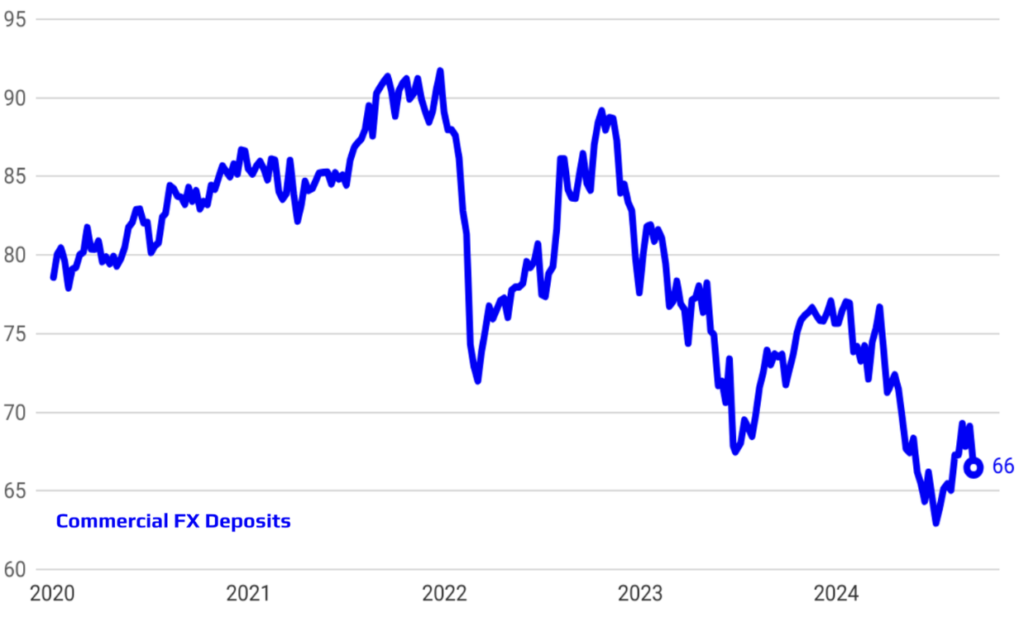
Rising Foreign Investor Interest and Successful Reserve Accumulation
Foreign investor interest in Turkish assets has been on the rise, reflecting growing confidence in the country’s economic prospects and policy direction. This renewed interest is evident in increased foreign participation in both the Turkish equity and bond markets. Simultaneously, the Central Bank’s reserve accumulation strategy has been effective, as evidenced by the robust increase in gross reserves. This approach not only bolsters Turkey’s financial resilience but also enhances its ability to manage external shocks. Together, these developments signal a strengthening of Turkey’s economic position and its attractiveness as a destination for international investment.
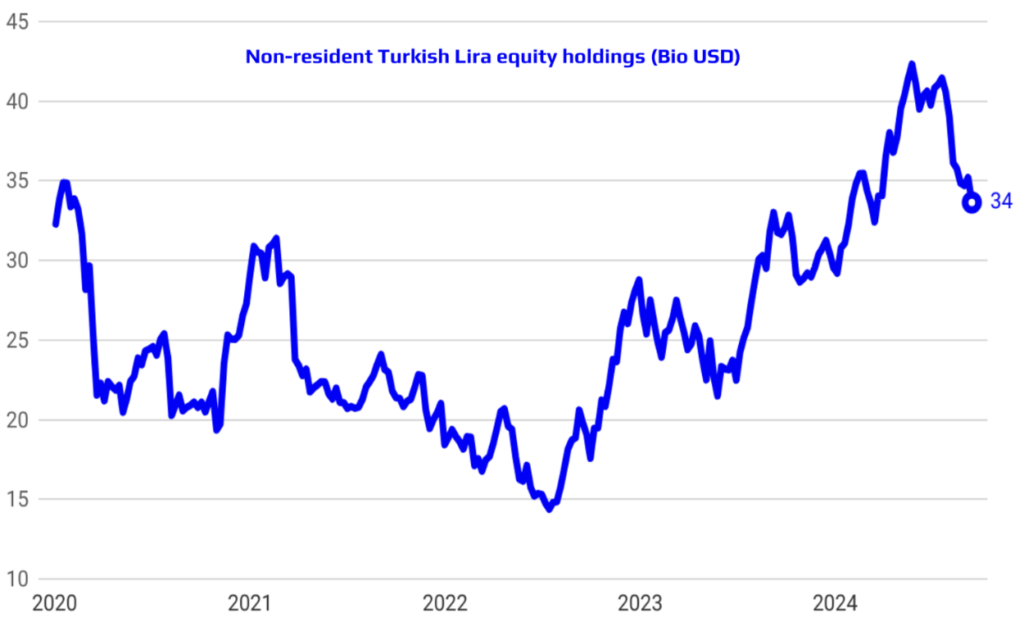
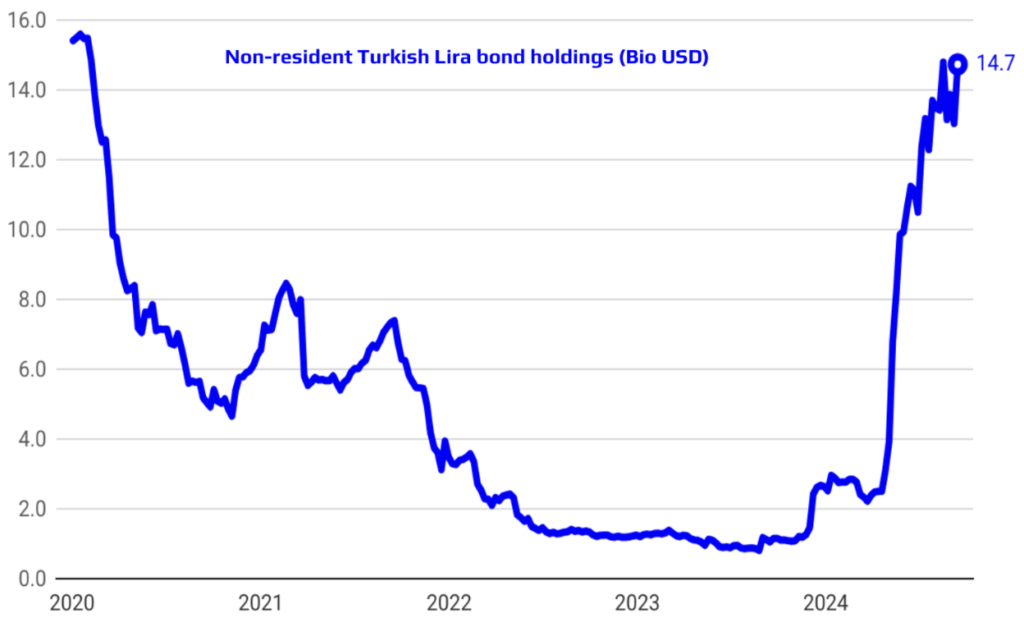
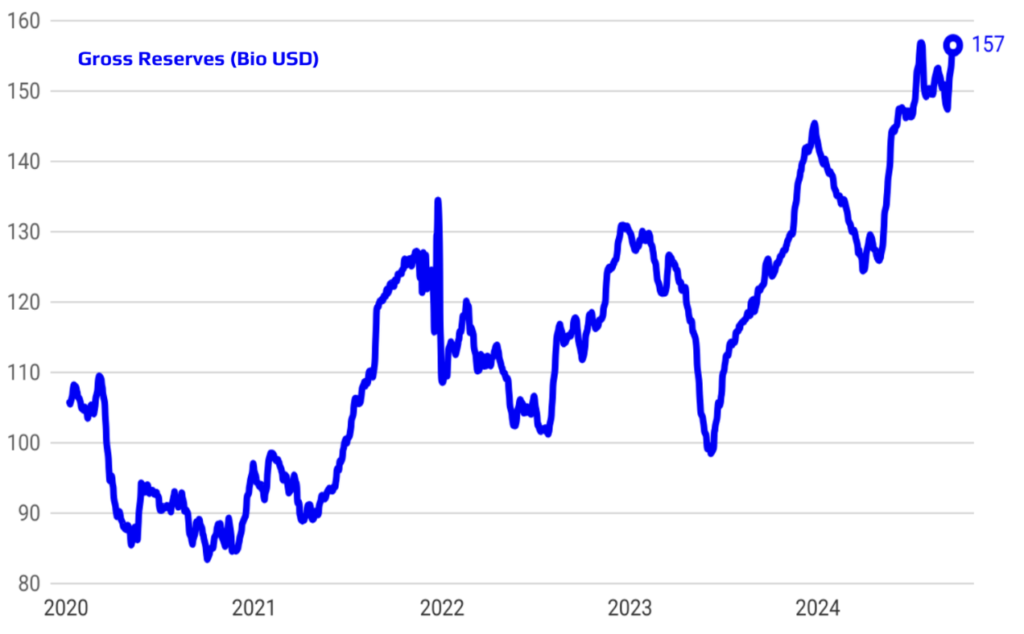
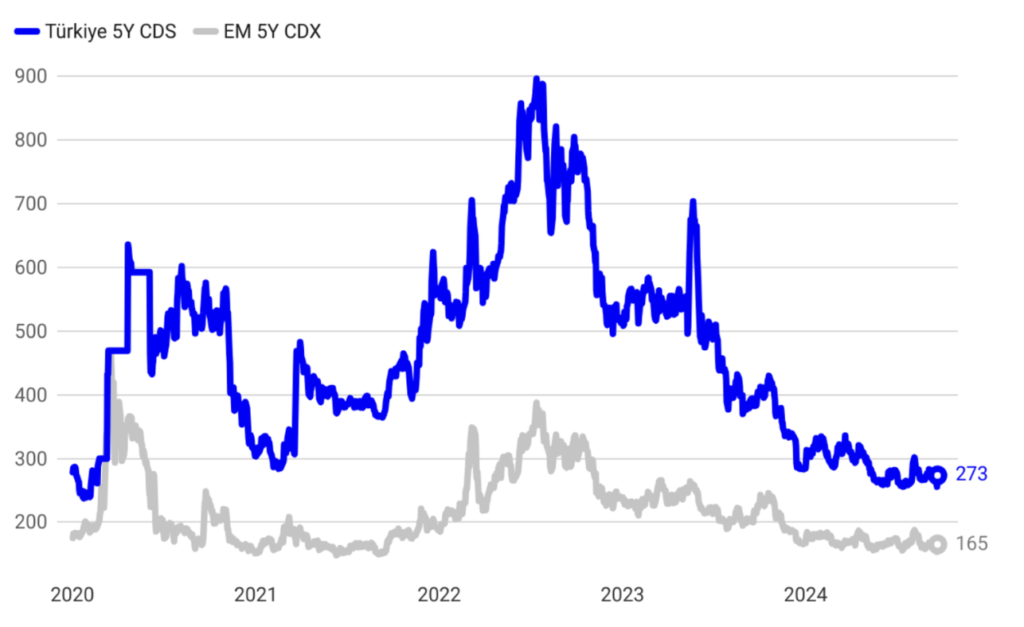
Strengthened Reserves and Credible Policies Drive Down Country Risk Premium
The strengthening of reserves, combined with the credibility of implemented policies, has led to a notable improvement in Turkey’s country risk premium. This positive shift reflects increased investor confidence in the stability and sustainability of Turkey’s economic outlook. As a result, the cost of external borrowing has significantly declined, making it more affordable for the country to finance its external obligations. This improved risk profile not only enhances Turkey’s access to international capital markets but also supports long-term financial stability and economic resilience.
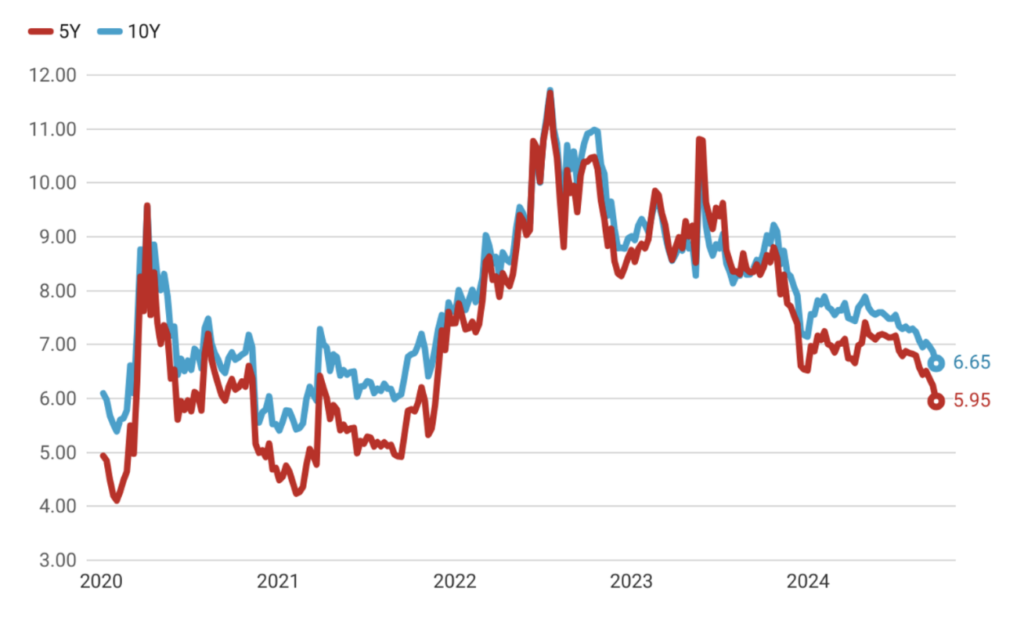
Achieving Real Exchange Rate Appreciation and Breaking the Depreciation Expectations
The implementation of policies aimed at achieving real exchange rate appreciation has effectively broken the prevailing expectations of continued depreciation of the Turkish Lira. This shift indicates a more balanced and sustainable exchange rate, boosting confidence in the local currency. Market forecasts now reflect an anticipated real appreciation of the TL, signaling that the currency’s value is expected to strengthen relative to its fundamentals. This development not only reduces inflationary pressures but also enhances the attractiveness of TL-denominated assets, contributing to a more stable and predictable financial environment.
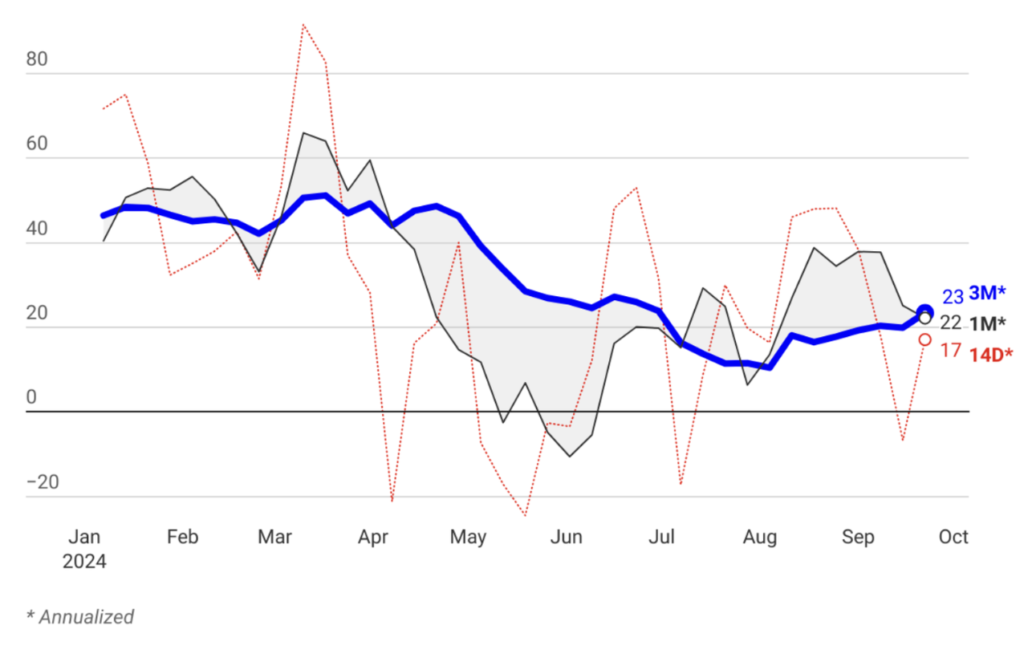
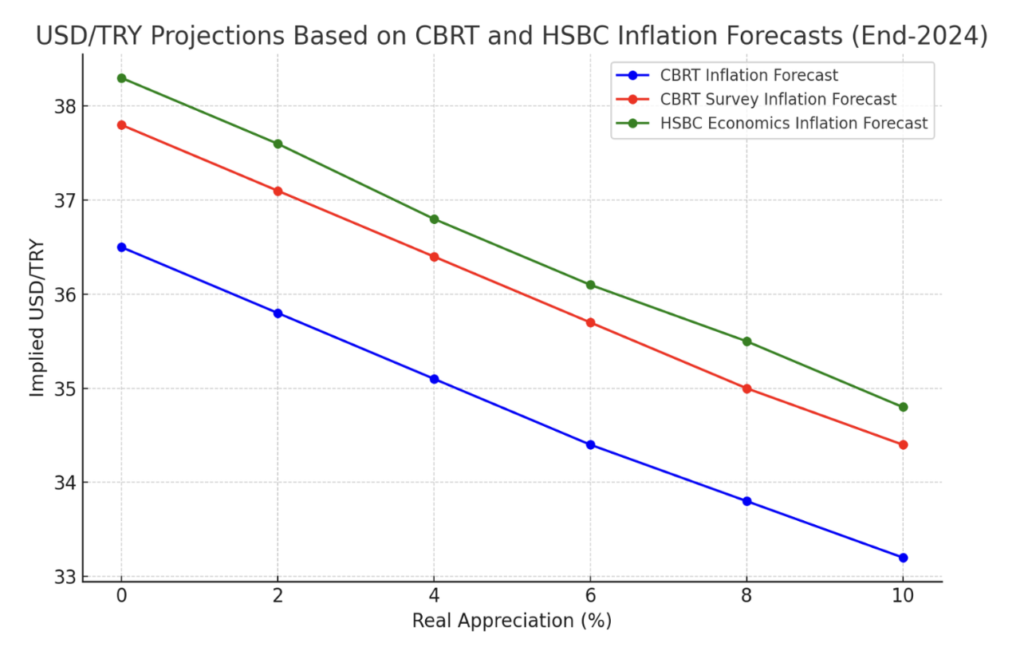
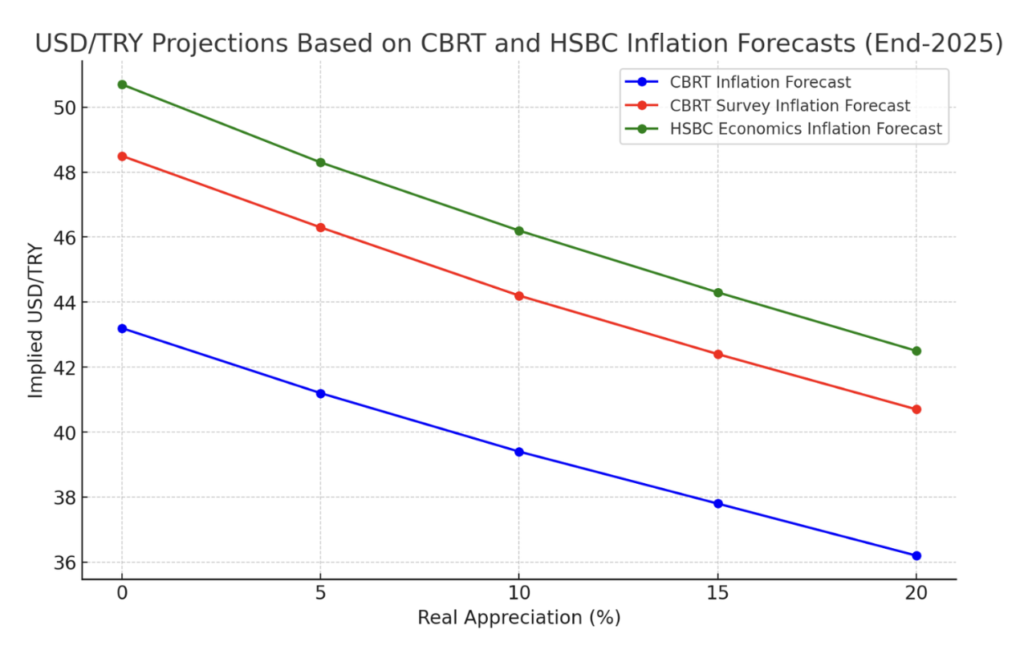
Strengthened Credibility of Tight Monetary Policy Anchors Inflation Expectations
The Central Bank’s commitment to maintaining its interest rates until a lasting improvement in inflation expectations is observed and has reinforced the credibility of its tight monetary policy stance. This firm approach has successfully anchored inflation expectations, signaling to markets and investors that the Bank is resolute in its fight against inflation. As a result, a downward trend in inflation is now anticipated, reflecting the effectiveness of these measures in stabilizing the economic outlook and fostering a predictable environment for future growth.
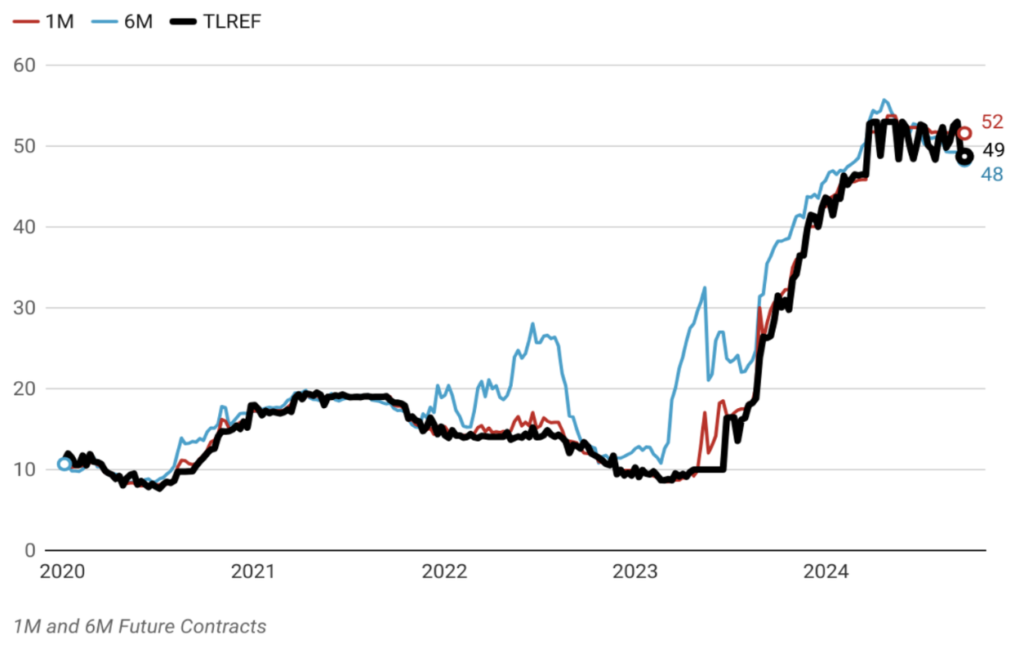
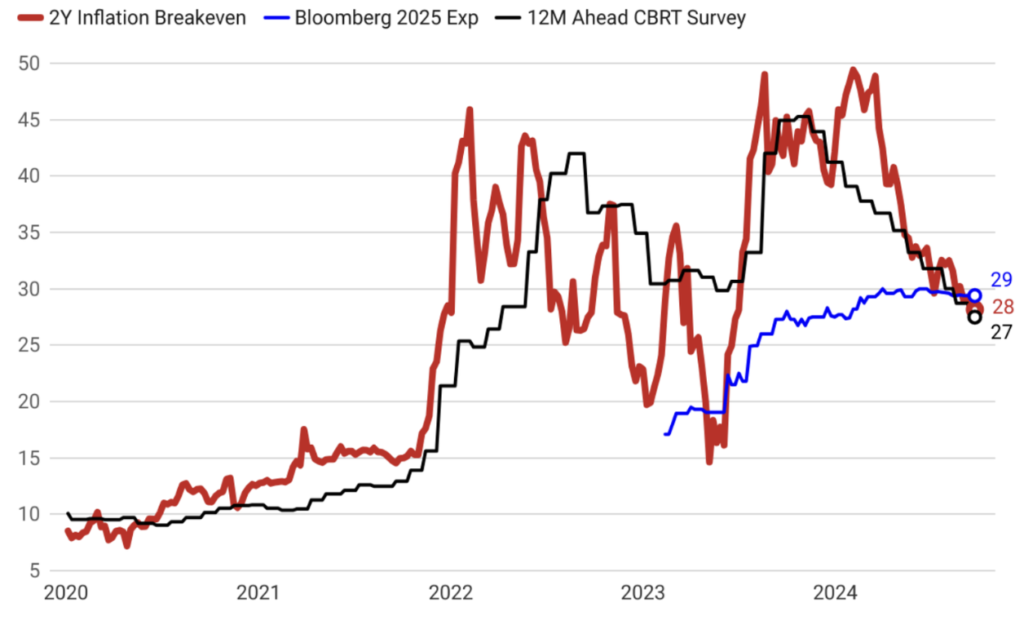
Consistent Economic Policy Framework Paves the Way for 2025 Macroeconomic Stability
The economic policy framework established by the current administration has been consistently structured and is expected to be implemented without deviation through 2025. This steadfast approach underscores the commitment to achieving the targeted macroeconomic stability, with a focus on sustaining balanced growth, reducing inflation, and maintaining fiscal discipline. By adhering to this coherent strategy, the administration aims to meet its macroeconomic objectives and foster a stable and predictable economic environment, providing a solid foundation for long-term prosperity and resilience.